暑假集训系列题解(十三)
暑假集训系列题解(十三)¶
题目1¶
题目链接¶
题目描述¶
Nuske has a grid with N rows and M columns of squares. The rows are numbered 1 through N from top to bottom, and the columns are numbered 1 through M from left to right. Each square in the grid is painted in either blue or white. If S_{i,j} is 1, the square at the i-th row and j-th column is blue; if S_{i,j} is 0, the square is white. For every pair of two blue square a and b, there is at most one path that starts from a, repeatedly proceeds to an adjacent (side by side) blue square and finally reaches b, without traversing the same square more than once.
Phantom Thnook, Nuske's eternal rival, gives Q queries to Nuske. The i-th query consists of four integers x_{i,1}, y_{i,1}, x_{i,2} and y_{i,2} and asks him the following: when the rectangular region of the grid bounded by (and including) the xi,1-th row, xi,2-th row, yi,1-th column and yi,2-th column is cut out, how many connected components consisting of blue squares there are in the region?
Process all the queries.
Constraints
1≤N,M≤2000
1≤Q≤200000
Si,j is either 0 or 1.
Si,j satisfies the condition explained in the statement.
1≤x_{i,1}≤x_{i,2}≤N(1≤i≤Q)
1≤y_{i,1}≤y_{i,2}≤M(1≤i≤Q)
输入¶
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M Q S1,1..S1,M : SN,1..SN,M x1,1 yi,1 xi,2 yi,2 : xQ,1 yQ,1 xQ,2 yQ,2
输出¶
For each query, print the number of the connected components consisting of blue squares in the region.
样例输入¶
样例输出¶
提示¶
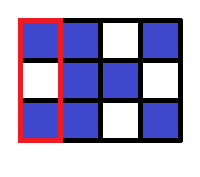
In the first query, the whole grid is specified. There are three components consisting of blue squares, and thus 3 should be printed.
In the second query, the region within the red frame is specified. There are two components consisting of blue squares, and thus 2 should be printed. Note that squares that belong to the same component in the original grid may belong to different components.
题解¶
前缀和以及树的性质,森林的个数等于点的个数减去边的数目,用前缀和维护边的数目和点的数目即可。
代码¶
#pragma GCC optimize(1)
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
char a[2050][2050] = {0};
int qzh[2050][2050] = {0};
int qzl[2050][2050] = {0};
int sum[2050][2050] = {0};
int main()
{
int n, m, q;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%s", a[i] + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
sum[i][j] = -sum[i - 1][j - 1] + sum[i][j - 1] + sum[i - 1][j] + a[i][j] - '0';
if (a[i][j] == '1')
{
int tmp1 = 0, tmp2 = 0;
if (a[i - 1][j] == '1')
tmp2++;
if (a[i][j - 1] == '1')
tmp1++;
qzh[i][j] = -qzh[i - 1][j - 1] + qzh[i][j - 1] + qzh[i - 1][j] + tmp1;
qzl[i][j] = -qzl[i - 1][j - 1] + qzl[i][j - 1] + qzl[i - 1][j] + tmp2;
}
else
{
qzh[i][j] = -qzh[i - 1][j - 1] + qzh[i][j - 1] + qzh[i - 1][j];
qzl[i][j] = -qzl[i - 1][j - 1] + qzl[i][j - 1] + qzl[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
while (q--)
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
int ans = sum[x2][y2] - sum[x1 - 1][y2] - sum[x2][y1 - 1] + sum[x1 - 1][y1 - 1];
ans = ans - (qzh[x2][y2] - qzh[x1 - 1][y2] - qzh[x2][y1] + qzh[x1 - 1][y1]);
ans = ans - (qzl[x2][y2] - qzl[x1][y2] - qzl[x2][y1 - 1] + qzl[x1][y1 - 1]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
题目2¶
题目链接¶
题目描述¶
Nukes has an integer that can be represented as the bitwise OR of one or more integers between A and B (inclusive). How many possible candidates of the value of Nukes's integer there are?
Constraints
1≤A≤B<2^{60}
A and B are integers.
输入¶
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
A
B
输出¶
Print the number of possible candidates of the value of Nukes's integer.
样例输入¶
样例输出¶
提示¶
In this case, A=7 and B=9. There are four integers that can be represented as the bitwise OR of a non-empty subset of {7, 8, 9}: 7, 8, 9 and 15.
题解¶
假设A,B两个数的二进制如下:
A:xxxxxx..0*****
B:xxxxxx..10-----
则:
C:xxxxxx..011111
D:xxxxxx..100000
C和D一定满足A<=C<=D<=B
则:
E:xxxxxx..1*****
F:xxxxxx..111111
G:xxxxxx..100111
其中[E,F]可以由[A,C]和D或运算得到,[D,G]可以由[D,B]或运算得到,所以答案即为[A,G]\cup[E,F]
代码¶
#pragma GCC optimize(1)
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
ll a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a > b)
swap(a, b);
ll tmp = b, aa = a;
for (ll i = 60; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (((a ^ b) >> i) & 1)
{
for (ll j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
tmp |= (1ll << j); ///等效于xxxxx..111111
a |= (1ll << i); ///等效于xxxxx..1*****
for (i--; i >= 0 && !((b >> i) & 1); i--)
;
for (; i >= 0; i--)
b |= (1ll << i); ///等效于xxxxx..100111
break;
}
}
ll ans = 0;
if (b >= a)
ans = tmp - aa + 1;
else
ans = tmp - a + 1 + b - aa + 1;
cout << ans << endl;
}
题目3¶
题目链接¶
题目描述¶
冬冬正和他的朋友一起玩抢占城堡的游戏,该游戏可以表示为大小为n×m的网格,每个格子最多只能容下一座城堡,每个格子有三种状态:
1、空城堡用“.”表示;
2、障碍物用“*”表示,所有玩家都不能通过它;
3、一名游戏玩家的编号即为数字x,表示该城堡被x占领。
游戏是按玩家编号从小到大轮流进行的,在每一轮中,玩家轮流扩张势力范围:首先,第一个玩家扩张,然后第二个玩家扩张,依此类推。扩张规则如下:
对于玩家现在拥有的每个城堡,可以扩张到附近的空城堡(未被人占领的)。
玩家i可以从他已占领的城堡向上、下、左、右四个方向扩张,且每名玩家都有一个攻击力si,如果能在si步内(含si)到达附近的空城堡则可以抢占该城堡。
当所有玩家都不能继续抢占的时候游戏结束,冬冬想知道游戏结束时每名玩家所占的城堡数是多少?
输入¶
第一行包含三个整数n,m和p(1≤n,m≤1000,1≤p≤9)表示网格的行和列以及玩家数量。
第二行包含p整数si(1≤si≤5000)表示每名玩家的扩张速度。
以下n行描述了游戏网格,每行由m个符号组成,其中'.'表示空城堡,'*'表示障碍们,数字x(1≤x≤p)表示由玩家x拥有的城堡。
保证每名玩家在网格上至少有一座城堡。
输出¶
输出p个整数,表示游戏结束后每名玩家抢占的城堡数量。
样例输入¶
样例输出¶
提示¶
对于10%的数据,1≤n,m≤1000,p=1。
对于20%的数据,1≤n,m≤1000,p=2。
对于100%的数据,1≤n,m≤1000,1≤p≤9,1≤si≤5000。
题解¶
BFS直接搜索即可,注意搜索技巧,扩展技巧。
代码¶
#pragma GCC optimize(1)
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
char a[1050][1050] = {0};
int s[20] = {0};
int ans[20] = {0};
int vis[1050][1050] = {0};
int n, m, p;
int dx[] = {0, 1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, 0, 1, -1};
struct node
{
int x, y;
};
queue<node> que[1005];
void bfs(int k)
{
for (int p = 1; p <= s[k]; p++)
{
int tmp = que[k].size();
if (tmp == 0)
break;
for (int i = 0; i < tmp; i++)
{
int x = que[k].front().x;
int y = que[k].front().y;
que[k].pop();
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
{
int xx = x + dx[j];
int yy = y + dy[j];
if (xx <= 0 || xx > n || yy <= 0 || yy > m || vis[xx][yy] != 0)
continue;
vis[xx][yy] = k;
que[k].push({xx, yy});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &p);
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++)
scanf("%d", &s[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%s", a[i] + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (a[i][j] == '.')
;
else
{
if (a[i][j] == '*')
{
vis[i][j] = -1;
}
else
{
vis[i][j] = a[i][j] - '0';
que[a[i][j] - '0'].push({i, j});
}
}
}
}
while (1)
{
int flag = 1;
for (int p1 = 1; p1 <= p; p1++)
{
if (que[p1].size() > 0)
{
bfs(p1);
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag)
break;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (vis[i][j] != -1)
ans[vis[i][j]]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++)
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
}