2020-09-21凸包算法
http://icpc.upc.edu.cn/problem.php?cid=2585&pid=7
题目描述¶
Recently, the nation was shocked by news of Sungai Kim Kim incident in Pasir Gudang, Johor, which has been polluted by chemical waste. Thousands of people who are affected had experienced nausea, dizziness and vomiting, and more than 100 schools were ordered to shut. In order to ensure that such incident will not happen again, an early warning system need o be developed so that residents can make early preparation, and authorities are able to move and act much faster.
A group of scientists has formed a committee to handle the incident, and a smart system with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors was suggested. Numerous sensors which can sense and monitor damages to the environment, either air or water, have been strategically installed around the state, and their coordinates are also recorded. However, the proposed system encountered a failure during its first testing phase. They want you to fix the problem in determining whether the given coordinates of sensors are safe or in the affected areas.
An affected area is defined as the polygon with the minimum length perimeter that can enclose all sensors that trigger warning signal within that area. For example, the sensors (represented by dots) of an affected area and its associated polygon, as well as safe (represented by triangles) and unsafe (represented by diamonds) points of the first dataset are illustrated below.
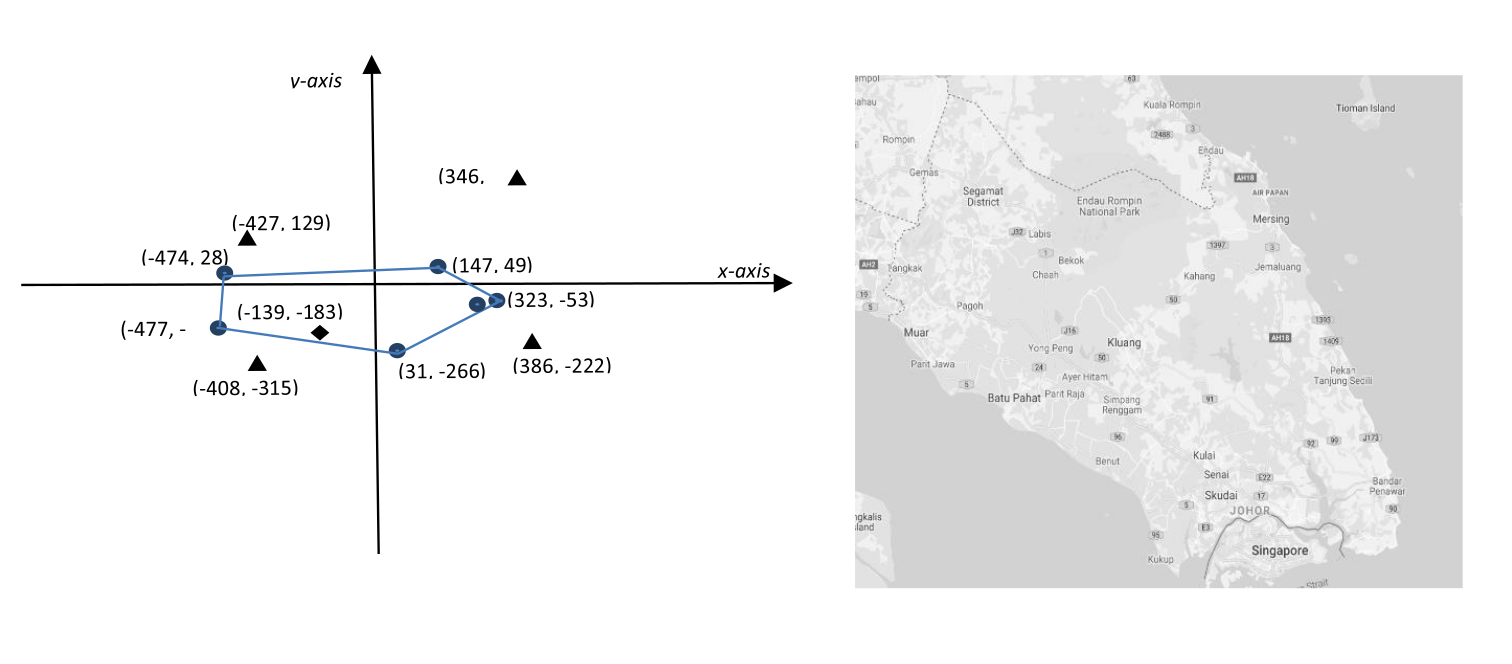
输入¶
The input will contain records of data for several test cases of affected areas. The first line of each data set contains a non-negative integer T, the number of test cases (1≤T≤50). Each test case starts with two non-negative integer C and P which is the number of coordinates (3≤C≤50), and points (1≤P≤50), respectively. The next C lines contain coordinates (x-coordinate, y-coordinate) of each installed sensor, separated with blank spaces. The following P lines contain coordinates (x-coordinate, y-coordinate) of certain locations in the state, separated with blank spaces. All coordinates are integers between −500 and 500 inclusive.
输出¶
For each test case, output the following item:
First line: The number of the test cases. The first record corresponds to Case1, the second to Case2 , etc.
Next line: A listing of all the points that appear on the perimeter of the affected area. The points must be identified in the standard form "x-coordinate y- coordinate". The listing must be oriented counter-clockwise and begin and end with the same point.
Last line: For each point of location in the data set, output the line:
x−coordinatey−coordinateisstatus where x−coordinatey−coordinate is the coordinate of the location from the input and status is ′safe′ or ′unsafe′. A location is considered unsafe it is within the sensor perimeter. A point in exactly at the edge of the perimeter is considered safe.
样例输入¶
2
6 5
-477 -180
31 -266
-474 28
147 49
323 -53
277 -79
346 488
-139 -183
-427 129
386 -222
-408 -315
5 2
-52 -325
104 420
315 356
-192 8
493 146
404 228
-239 484
样例输出¶
Case 1
-477 -180
31 -266
323 -53
147 49
-474 28
-477 -180
346 488 is safe!
-139 -183 is unsafe!
-427 129 is safe!
386 -222 is safe!
-408 -315 is safe!
Case 2
-192 8
-52 -325
493 146
315 356
104 420
-192 8
404 228 is unsafe!
-239 484 is safe!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e3+9;
const int mod=1e9+7;
struct node
{
double x,y;
};
struct point
{
double x,y;
point friend operator - (point a,point b)
{
return {a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y};
}
} p[maxn],s[maxn],query[maxn];
double dis(point a,point b)
{
point c=a-b;
return sqrt(c.x*c.x+c.y*c.y);
}
double chax(point a,point b)//叉乘
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
double mulx(point p1,point p2,point p3)
{
return chax(p2-p1,p3-p1);
}
bool cmp2(point a,point b)
{
if (a.x!=b.x)
return a.x<b.x;
return a.y<b.y;
}
double xxx,yyy;
vector<node>v;
int judge(int i,int j,int k)
{
double xpa=xxx-v[i].x;
double ypa=yyy-v[i].y;
double xpb=xxx-v[j].x;
double ypb=yyy-v[j].y;
double xpc=xxx-v[k].x;
double ypc=yyy-v[k].y;
double ans1=xpa*ypb-xpb*ypa;
double ans2=xpb*ypc-xpc*ypb;
double ans3=xpc*ypa-xpa*ypc;
if(ans1==0||ans2==0||ans3==0)
return 1;
if(ans1>0&&ans2>0&&ans3>0)
return 1;
if(ans1<0&&ans2<0&&ans3<0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int hack(int i,int j)
{
double xpa=xxx-v[i].x;
double ypa=yyy-v[i].y;
double xpb=xxx-v[j].x;
double ypb=yyy-v[j].y;
double ans1=xpa*ypb-xpb*ypa;
if(ans1==0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
int cas=0;
for(int j=1;j<=T;j++)
{
v.clear();
int n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>p[i].x>>p[i].y;
}
sort(p,p+n,cmp2);
int m=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
while(m>1&&mulx(s[m-2],s[m-1],p[i])<=0) m--;
s[m++]=p[i];
}
int kk=m;
for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--)
{
while(m>kk&&mulx(s[m-2],s[m-1],p[i])<=0) m--;
s[m++]=p[i];
}
if(n>1)
m--;
printf("Case %d\n",j);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
cout<<s[i].x<<" "<<s[i].y<<endl;
v.push_back({s[i].x,s[i].y});
}
cout<<s[0].x<<" "<<s[0].y<<endl;
for(int ii=1; ii<=q; ii++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&xxx,&yyy);
int flag=1;
for(int i=0; i<v.size()&&flag; i++)
{
for(int j=i+1; j<v.size()&&flag; j++)
{
for(int k=j+1; k<v.size()&&flag; k++)
{
if(judge(i,j,k))
{
flag=0;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<v.size()-1&&!flag; i++)
if(hack(i,i+1))
flag=1;
if(hack(v.size()-1,0))
flag=1;
if(!flag)
{
printf("%.0f %.0f is unsafe!\n",xxx,yyy);
}
else
{
printf("%.0f %.0f is safe!\n",xxx,yyy);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//AndrewScan
/*
* @Author: lzyws739307453
* @Language: C++
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 105;
const double eps = 1e-8;
typedef struct Point {
double x, y;
Point(double x_ = 0, double y_ = 0) : x(x_), y(y_) {}
bool operator < (const Point& s) const {
return x != s.x ? x < s.x : y < s.y;
}
}vect;
struct Point p[MAXN], S[MAXN], s;
int sgn(double x) {
return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps ? 1 : 0;
}
vect operator - (const Point a, const Point b) {
return vect(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
double Cross(const vect a, const vect b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dist(const Point a, const Point b) {
return sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y));
}
bool Onleft(const Point a, const Point b, const Point c) {
return sgn(Cross(b - a, c - a)) > 0;
}
bool InTB(const Point p[], const Point s, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % n;
if (Cross(p[j] - p[i], s - p[i]) <= 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
int AndrewScan(Point p[], int n) {
sort(p, p + n);
int top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (top > 1 && !Onleft(S[top - 2], S[top - 1], p[i]))
top--;
S[top++] = p[i];
}
int tmp = top;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
while (top > tmp && !Onleft(S[top - 2], S[top - 1], p[i]))
top--;
S[top++] = p[i];
}
return top;
}
int main() {
int n, q, t, cnt, kase = 0;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
cnt = AndrewScan(p, n);
if (n > 1)
cnt--;
if (kase)
printf("\n");
printf("Case %d\n", ++kase);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
printf("%.0lf %.0lf\n", S[i].x, S[i].y);
printf("%.0lf %.0lf\n", S[0].x, S[0].y);
while (q--) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &s.x, &s.y);
printf("%.0lf %.0lf ", s.x, s.y);
if (InTB(S, s, cnt))
printf("is unsafe!\n");
else printf("is safe!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define PI 3.1415926535
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x,y;
};
node vex[1000];//存入的所有的点
node stackk[1000];//凸包中所有的点
int xx,yy;
bool cmp1(node a,node b)//排序找第一个点
{
if(a.y==b.y)
return a.x<b.x;
else
return a.y<b.y;
}
int cross(node a,node b,node c)//计算叉积
{
return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(c.x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y);
}
double dis(node a,node b)//计算距离
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)*1.0+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
bool cmp2(node a,node b)//极角排序另一种方法,速度快
{
if(atan2(a.y-yy,a.x-xx)!=atan2(b.y-yy,b.x-xx))
return (atan2(a.y-yy,a.x-xx))<(atan2(b.y-yy,b.x-xx));
return a.x<b.x;
}
bool cmp(node a,node b)//极角排序
{
int m=cross(vex[0],a,b);
if(m>0)
return 1;
else if(m==0&&dis(vex[0],a)-dis(vex[0],b)<=0)
return 1;
else return 0;
/*if(m==0)
return dis(vex[0],a)-dis(vex[0],b)<=0?true:false;
else
return m>0?true:false;*/
}
int main()
{
int t,L;
while(~scanf("%d",&t),t)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<t; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&vex[i].x,&vex[i].y);
}
if(t==1)
printf("%.2f\n",0.00);
else if(t==2)
printf("%.2f\n",dis(vex[0],vex[1]));
else
{
memset(stackk,0,sizeof(stackk));
sort(vex,vex+t,cmp1);
stackk[0]=vex[0];
xx=stackk[0].x;
yy=stackk[0].y;
sort(vex+1,vex+t,cmp2);//cmp2是更快的,cmp更容易理解
stackk[1]=vex[1];//将凸包中的第两个点存入凸包的结构体中
int top=1;//最后凸包中拥有点的个数
for(i=2; i<t; i++)
{
while(i>=1&&cross(stackk[top-1],stackk[top],vex[i])<0) //对使用极角排序的i>=1有时可以不用,但加上总是好的
top--;
stackk[++top]=vex[i]; //控制<0或<=0可以控制重点,共线的,具体视题目而定。
}
double s=0;
//for(i=1; i<=top; i++)//输出凸包上的点
//cout<<stackk[i].x<<" "<<stackk[i].y<<endl;
for(i=1; i<=top; i++) //计算凸包的周长
s+=dis(stackk[i-1],stackk[i]);
s+=dis(stackk[top],vex[0]);//最后一个点和第一个点之间的距离
/*s+=2*PI*L;
int ans=s+0.5;//四舍五入
printf("%d\n",ans);*/
printf("%.2lf\n",s);
}
}
}